Amblyopia, commonly known as “lazy eye,” is a term that might sound familiar to many parents. This condition occurs when one eye does not develop proper vision, leading to poor visual acuity that cannot be corrected by glasses or contact lenses. In most cases, the brain favours the stronger eye, often ignoring or suppressing the weaker one.
Early detection and intervention are crucial, as successful treatment can often restore vision if addressed early. As a parent, it’s important to keep an eye on your child’s vision and book regular checkups to promote healthy visual development.
Understanding Amblyopia
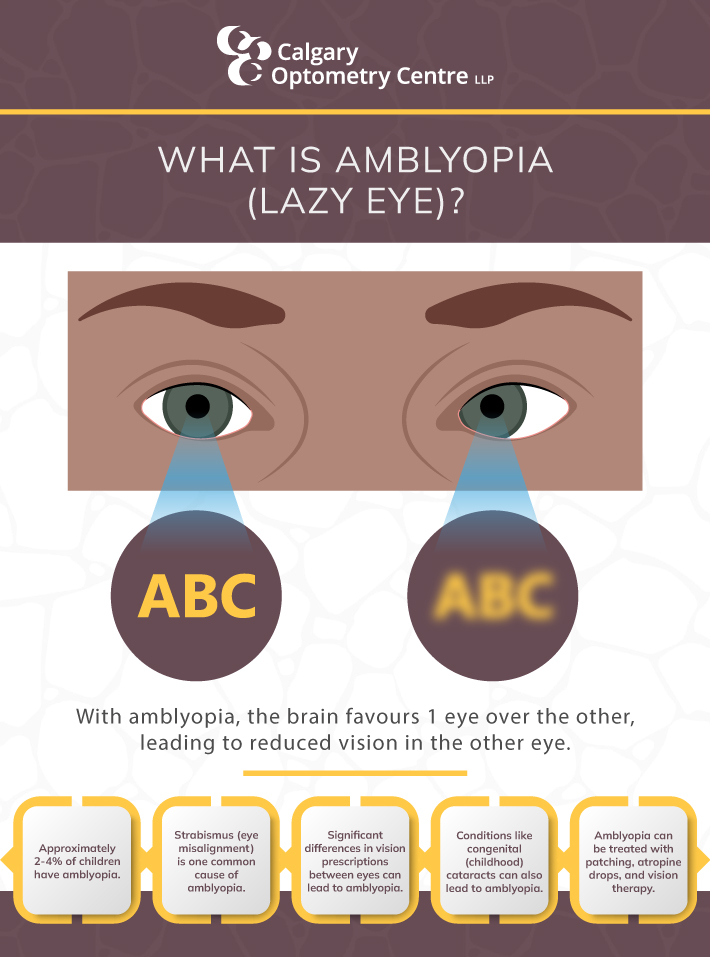
Amblyopia affects approximately 2–4% of children, making it one of the most prevalent vision disorders in children across North America. However, many children go undiagnosed, which can lead to long-term vision impairment.
This condition typically develops in childhood when the nerve pathways between the brain and eyes aren’t properly stimulated. Without proper stimulation, the brain begins to favour one eye over the other, leading to reduced vision in the affected eye.
The degree of vision impairment can vary significantly from one individual to another; some children may have very limited vision in the amblyopic eye, while others might retain some functional sight. However, since the brain tends to favour the stronger eye, a child may primarily rely on this eye for visual tasks, leading to underutilization of the amblyopic eye.
The Role of Vision Development
Vision development is a critical part of a child’s growth. During early childhood, the visual system undergoes rapid development, establishing connections between the eyes and the brain. Any disruption in this process can potentially lead to conditions like amblyopia, so early detection is vital for effective intervention.
What Causes Amblyopia?
The primary cause of amblyopia is often related to improper nerve pathway development. This can occur due to several factors:
- Strabismus (misalignment of the eyes): When the eyes do not align properly, the brain may ignore input from one eye to avoid double vision.
- Unequal refractive errors: Significant differences in vision prescriptions between the 2 eyes can lead to amblyopia if one eye consistently receives better visual input than the other.
- Deprivation amblyopia: Conditions like cataracts can obstruct vision in one eye, leading to amblyopia.
Detecting & Treating Amblyopia
Early detection is critical for effectively treating amblyopia. Regular eye exams can help identify amblyopia early when interventions are most successful. During a comprehensive eye exam, eye care professionals use a variety of methods to detect amblyopia.
Initially, they will assess visual acuity by having a child read letters or symbols on an eye chart, noting any differences in vision between the eyes. Additionally, the doctor may perform a cover test, where 1 eye is covered while the other is observed for any movement or shift; this helps determine if strabismus (crossed eyes) is present.
Common Treatments for Amblyopia
Effective treatment of amblyopia requires a tailored approach based on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. The goal of treatment is to encourage proper vision development in the affected eye, allowing it to strengthen and function more effectively alongside the stronger eye.
Patching
This method involves placing a patch over the stronger eye for a specified period to encourage the use of the weaker eye. By forcing the brain to rely on the amblyopic eye, patching helps to strengthen its visual capabilities over time. Consistency and patience are key components of this therapy, as improvements may take weeks or months to manifest.
Atropine Eye Drops
Atropine is a medication that blurs the vision of the stronger eye, encouraging the child to use the weaker eye. Typically administered once a day, this treatment promotes the visual development of the amblyopic eye while encouraging equal use of both eyes.
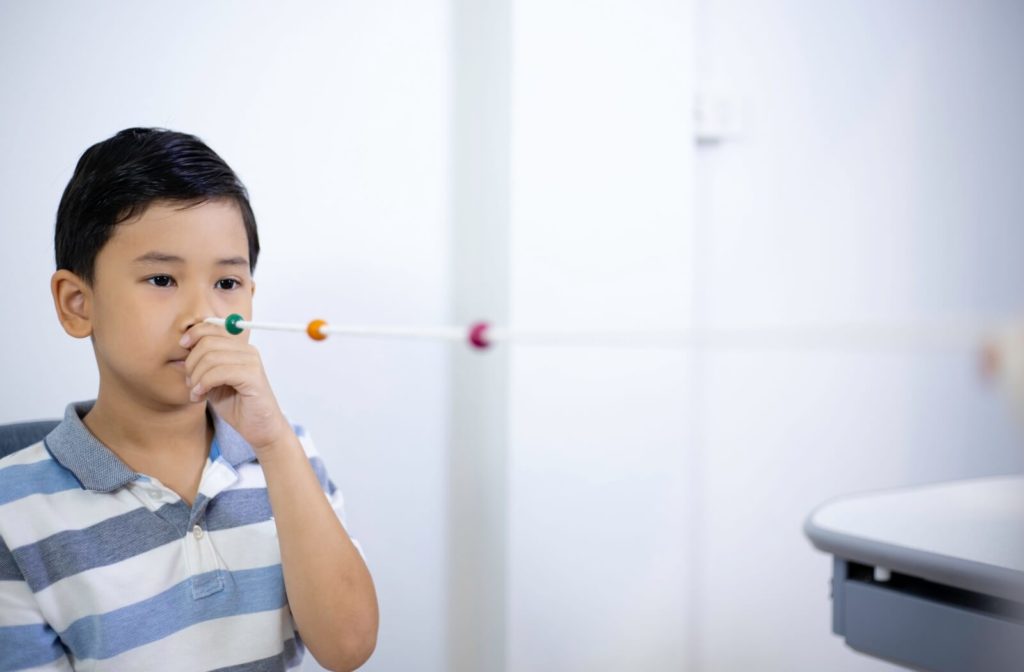

Vision Therapy
This involves a series of exercises designed to enhance the visual skills of the amblyopic eye. Vision therapy may include activities that improve eye coordination, focusing, and tracking abilities and exercises tailored to strengthen the neural pathways between the eyes and the brain. The goal is to facilitate better cooperation between the eyes and improve overall visual function.
Surgical Intervention
In certain cases where strabismus is present, surgery may be recommended to correct the alignment. This surgical approach aims to enhance the ability of the eyes to work together, which is crucial for effective vision development. Post-surgery, other treatments such as patching or vision therapy may still be beneficial to help achieve optimal outcomes.
What Happens if Amblyopia Is Left Untreated?
If amblyopia is not addressed, it can lead to some vision difficulties, particularly in the affected eye. Children may struggle with depth perception and visual acuity, which can affect everyday activities such as reading, sports, or driving as they grow older.
However, it’s important to remember that many individuals with amblyopia can still lead fulfilling lives with a range of activities they enjoy. The earlier amblyopia is detected and treated, the better the visual outcome will likely be. Regular eye exams and being proactive about vision concerns can help manage amblyopia effectively and provide a bright future for your child’s vision.
Book a Checkup for Your Child
Understanding amblyopia and its potential impacts is vital for parents in safeguarding their children’s vision health. Early detection can prevent long-term vision issues. If you suspect your child may have amblyopia, don’t wait—seek professional advice.
At Calgary Optometry Centre, we are dedicated to helping you understand and address vision concerns. Book an appointment with us today to check in on your child’s vision and help keep it on the right track.




